Comprehensive Guide to Raised Floor Systems
A raised floor system (also known as access flooring) is an elevated structural floor that sits above a solid substrate (like a concrete slab), creating a space (or void) for services like electrical wiring, HVAC systems, and cabling to run beneath the floor. This system is widely used in commercial buildings, data centers, and office spaces due to its flexibility, functionality, and ease of access for maintenance.
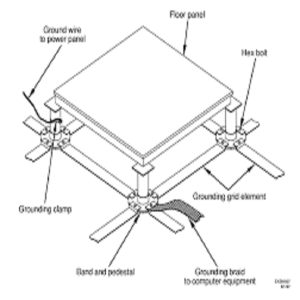
Key Components of a Raised Floor System
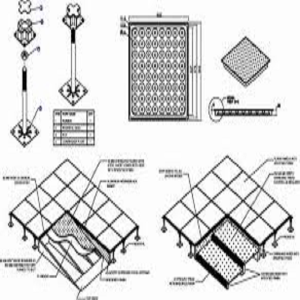
- Floor Panels
Raised floor panels form the walking surface of the system. These panels come in various materials such as steel, concrete, or composite materials. Typically, they are designed to be modular, allowing them to be lifted easily for access to the void beneath. Common types of raised floor panels include:- Steel Encapsulated Panels: Durable and ideal for high-traffic areas.
- Wood Core Panels: Lightweight with excellent fire-resistant properties.
- Perforated Panels: Allow airflow and cooling, often used in data centers.
- Pedestals
Pedestals are adjustable vertical supports that anchor the raised floor panels to the substrate. They determine the height of the floor and can vary from a few centimeters to over a meter, depending on the needs of the space. The height of the pedestals can be adjusted to accommodate more cabling or airflow. - Stringers
Stringers are horizontal bars that connect pedestals to each other. They provide added stability to the raised floor system, especially for areas with heavy loads like server rooms. Stringers are typically used when extra strength is required. - Underfloor Cavity
The space beneath the raised floor, known as the underfloor cavity or void, is used to run cabling, HVAC ducts, and plumbing. This void provides easy access to utilities, making it simpler to install, repair, or replace these systems.
Types of Raised Floor Systems
- Standard Raised Floors
Used primarily in office spaces and commercial buildings, standard raised floors are designed for cable management, data cabling, and power distribution. These systems typically feature solid, non-perforated panels and are ideal for flexible work environments. - Perforated Raised Floors
These floors feature perforated panels, allowing air to circulate through the underfloor cavity. Perforated raised floors are essential in data centers or server rooms, where cooling is critical to prevent overheating of equipment. - Anti-Static Raised Floors
Used in sensitive environments such as data centers or laboratories, anti-static raised floors help reduce electrostatic discharge (ESD), which can damage sensitive electronic equipment.
Benefits of a Raised Floor System
- Cable Management & Flexibility
Raised floors offer a flexible solution for managing cables, wires, and power distribution. They allow easy access for changes, reconfiguration, or repairs, making them ideal for offices and spaces with changing layouts. - Improved Airflow
Raised floors with perforated panels help manage airflow, which is essential for cooling equipment in data centers and IT environments. The underfloor void acts as a plenum, distributing cool air efficiently. - Easy Maintenance & Upgrades
One of the greatest advantages of raised floor systems is the ability to lift panels and access the underfloor cavity for repairs or upgrades. This ensures minimal disruption during maintenance and lowers downtime for businesses. - Aesthetic Appeal
Raised floor systems can be finished with a variety of materials such as carpet, vinyl, or laminate, allowing you to maintain an aesthetically pleasing environment without compromising on functionality. - Future-Proofing
With growing technology needs, raised floors offer a long-term solution by allowing for easy infrastructure upgrades, such as adding new data lines or electrical outlets.
Applications of Raised Floor Systems
- Data Centers & Server Rooms
Raised floor systems are essential in data centers to handle the vast amount of cabling and airflow required to cool servers. The underfloor space provides a plenum for conditioned air, ensuring optimal temperatures for equipment. - Offices & Commercial Buildings
Raised floors offer flexibility for ever-changing office environments. Businesses can easily reconfigure spaces, install new workstations, or add new technologies without needing major construction. - Telecommunications & Control Rooms
For environments with complex wiring and control systems, such as broadcast studios or command centers, raised floors provide easy access to critical infrastructure. - Educational Facilities & Laboratories
Universities and research centers benefit from raised floor systems for managing extensive data and power networks, making it easy to adapt to new technology requirements.
Optional Accessories & Features
- Cable Trays & Ladders
Cable trays and ladders are installed beneath the floor to organize and support large amounts of cabling. They provide structured pathways for cables, ensuring that everything remains organized and easy to access. - Grommets & Air Guards
Grommets are openings in the floor panels that allow cables to pass through, while air guards help prevent air leakage through the grommets, ensuring efficient cooling and minimizing energy loss. - Pushup Boxes & Power Outlets
Electrical and data outlets can be seamlessly integrated into raised floor systems using pushup boxes, providing easy access to power and data points without compromising the floor’s surface. - Panel Lifters
Panel lifters are essential tools used to easily lift and remove floor panels, allowing quick access to the void below for maintenance or repairs.
Installation Considerations
When installing a raised floor system, it’s important to consider:
- Load Capacity: Ensure the system can handle the weight of equipment and foot traffic.
- Height Requirements: The required height of the void will depend on the amount of cabling, air ducts, or piping that needs to be housed beneath the floor.
- Ventilation: If cooling is a concern, perforated or grated panels should be installed to allow for adequate airflow.
Why Choose a Raised Floor System?
A raised floor system is not just about elevating your flooring—it’s a practical solution to manage the growing complexity of modern infrastructure. Whether you need improved airflow, better cable management, or future-proofing for your workspace, raised floors provide flexibility, organization, and enhanced functionality for a wide range of applications.
By investing in a raised floor system, you ensure that your workspace remains adaptable to the technological demands of the future, all while keeping the aesthetics and cleanliness of your environment intact.
For more information on raised floor solutions or to inquire about installation, contact us at Raised Floor BD.